Lyssomanes viridis (Walckenaer, 1837) – Magnolia Green Jumper
Richman, Cutler& Hill 2012
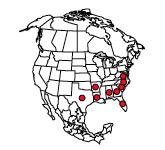
Most salticids are members of the Salticoid lineage. Lyssomanines form a separate, largely Old World group, whose appearance is noticeably different from typical jumpers. One of two New World genera, Lyssomanes spiders occur mainly in South and Central America. The single representative in North America is Lyssomanes viridis. While fairly common in the southeastern U.S. this spider is apparently expanding its range northward. The individuals shown here were found in the mid-Atlantic region at Cape May Point and Ocean View, NJ. The nearly transparent pigmentation of Lyssomanes viridis reveals features of their AME (Anterior Median Eyes) not easily noticeable in other jumpers. Each eye’s external lens is fixed and forms part of the outer cuticle. The retina lies behind the lens and has a series of attached muscles that can move the retina in an arc of approximately 60 degrees. While the field of view for each eye is fairly narrow the movable retinas allow the jumper to do relatively high resolution scanning of large objects. The changing colors seen in the jumper’s eyes are caused by variation in reflected light as the spider scans an object.
Edwards and Hill, 2008; Foelix, 1998


